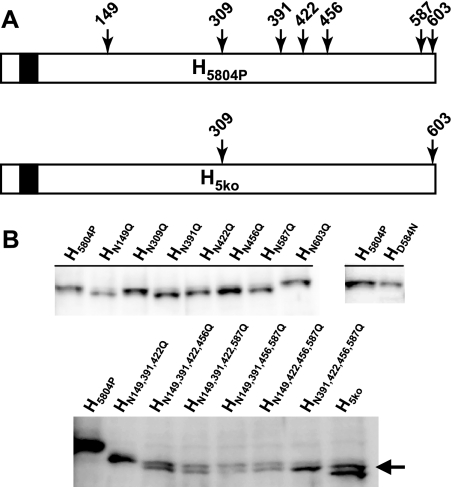
FIG. 3.
Systematic deglycosylation of H5804P. (A) Schematic drawing of the N-glycosylation sites of the type N-X-S/T located in the ectodomain of H5804P and the mutant protein H5ko. Protein schematics are shown from the N terminus (left) to the C terminus (right). The N-terminal white boxes represent the cytoplasmic tail, the black boxes the transmembrane domain, and the C-terminal white boxes the ectodomain. (B) Western blot expression analysis of a comprehensive panel of N-glycosylation knockout mutant H5804P proteins. Proteins were expressed by transfection of expression plasmids in Vero dogSLAMtag cells. (Top) Single N-glycan knockout proteins (left blot) and the HD584N knock-in mutant protein (right blot) compared to H5804P protein. Note that HN309Q, HN603Q, and HD584N do not shift in apparent molecular weight. (Bottom) Quadruple- and quintuple-knockout proteins produced in all possible combinations. Mutant proteins are shown with H5804P and HN149,391,422Q to illustrate the observed molecular weight shift. The arrow indicates the higher-molecular-weight band observed for H5ko.