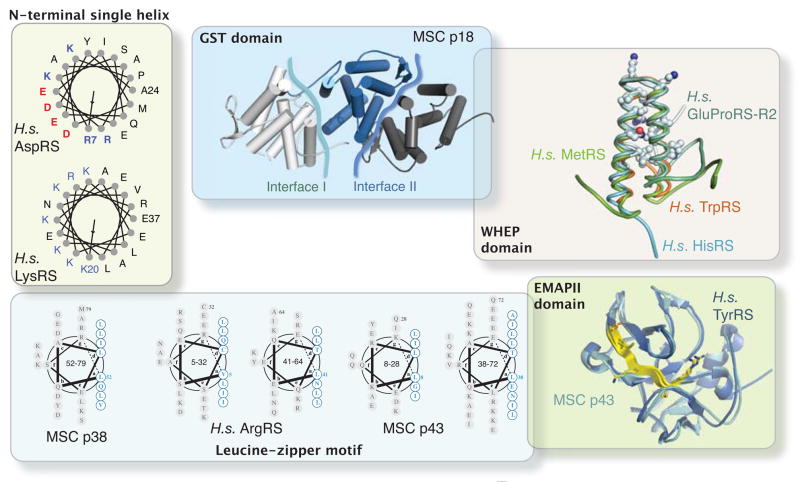
Figure 2.
Structures of appended domain/motifs in human AARSs and associated factors. These appended structures provide extra interfaces for protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions, and are critical for the expanded functions of human AARSs. N-terminal single helices of human AspRS and LysRS are shown to illustrate the amphiphilic nature of those helices. Two protein-protein interaction interfaces are shown as irregular blue lines on MSC p18 (PDB 2uz8). Conserved residues among WHEP domains in different AARSs are shown as sticks (PDB 1x59, 16t, 2djv for human HisRS, TrpRS and MetRS, respectively, and PDB 1r1b for the second WHEP domain (R2) in GluProRS,). The putative cytokine motifs on EMAP II structures of human TyrRS (PDB 1ntg) and MSC p43 (PDB 1fl0) are shown in yellow.