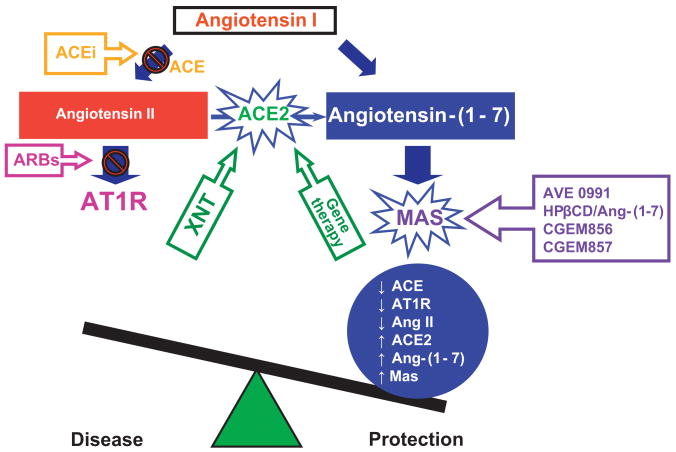
Figure.
Schematic diagram showing the counterregulatory axes of the RAS: ACE-AngII-AT1 receptor and ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas receptor. The ACEs play a central role in balancing the activity of these axes. While ACE degrades AngI to form AngII, ACE2 hydrolyzes AngII to produce Ang-(1-7). AVE 0991, HPβCD/Ang-(1-7), CGEM856 and CGEM857 are Ang-(1-7) analogues and, consequently, Mas agonists and XNT is an ACE2 activator. ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; ACEi: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; Ang: angiotensin; ARBs: AT1R blockers; AT1R: angiotensin II type 1 receptor.