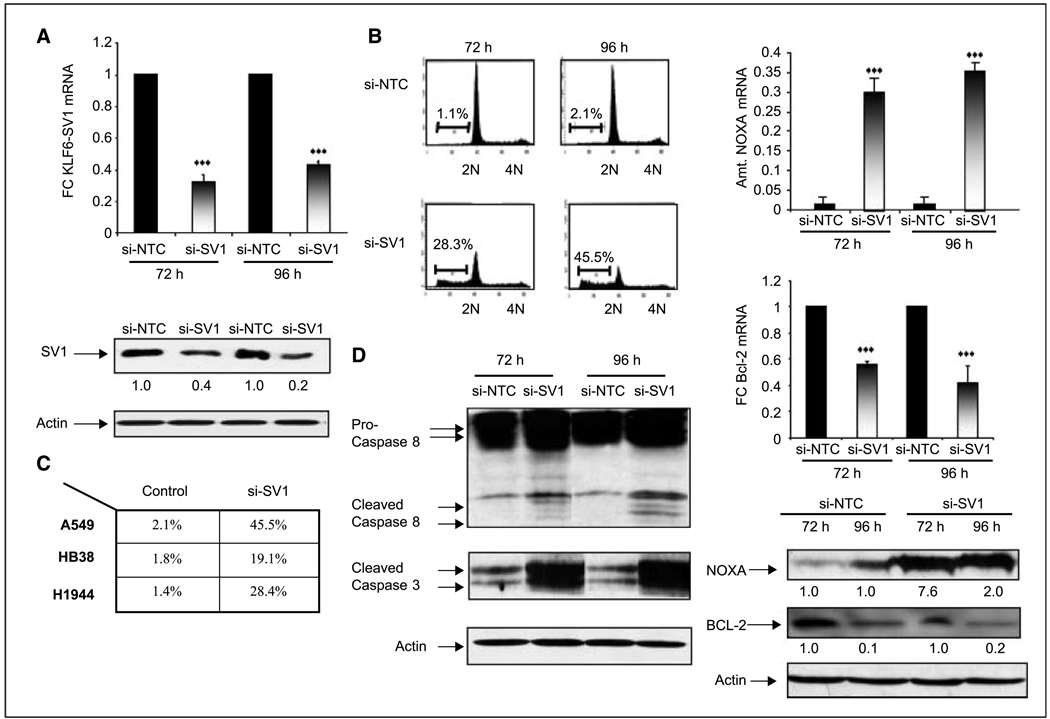
Figure 2.
Targeted reduction of KLF6-SV1 results in a marked increase in spontaneous apoptosis via activation of the intrinsic and extrinsic cell death pathways. A, qtRT-PCR and Western blot analysis of the A549 cell line transfected with a nontargeting control (si-NTC) and a siRNA specific to KLF6-SV1 (si-SV1) show significant down-regulation of KLF6-SV1 at both the mRNA and protein level at both 72 and 96 h; ***, P < 0.001. B and C, FACS analysis of si-NTC– and si-SV1–transfected A549 cells at 72 and 96 h. Targeted reduction of KLF6-SV1 results in a marked increase in spontaneous apoptosis in three independent lung cancer cell lines. Columns, mean of three independent experiments; bars, SD. D, si-SV1 activates both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. Western blot analysis shows a marked up-regulation of Caspase 3 and 8 in si-SV1–transfected A549 cell lines. qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis of si-NTC– and si-SV1–transfected cells for NOXA and Bcl-2 shows marked up-regulation of the proapoptotic NOXA (***, P < 0.0001) with concomitant down-regulation of Bcl-2 (***, P < 0.0001).