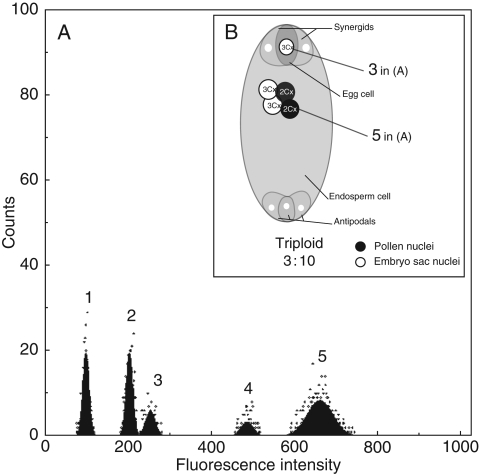
Fig. 3.
(A) Histogram of FCSS with five peaks: 1 and 2, standard Zea mays in the G1 and G2 phase, respectively; 3–5, Ranunculus kuepferi (Rk): 3, 3 Cx, embryo G1 phase; 4, embryo G2 phase; 5, 10 Cx endosperm (peak G1 phase). (B) Scheme of the respective embryo sac after fertilization, illustrating a triploid unfertilized embryo corresponding to peak 3, and the 10 Cx endosperm corresponding to peak 5. Since the mother plant was tetraploid, the embryo sac must have developed via a disturbed meiosis. The 3x em developed without fertilization, the endosperm via pseudogamy.