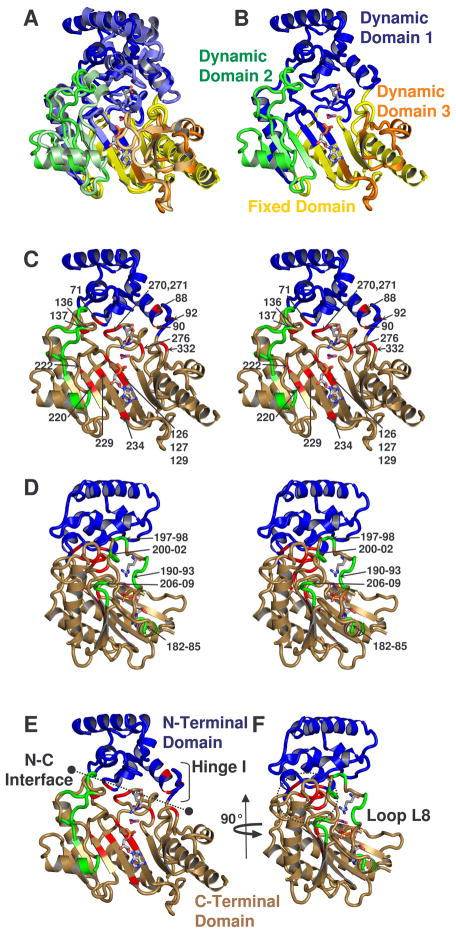
Figure 4.
(a) Comparison of the dynamic domains of substrate-free and -bound structures of arginine kinase (Yousef et al., 2003; Zhou et al., 1998). Dynamic domains 1, 2, and 3 are colored respectively blue, green and orange. The darker shade of each color is substrate-free and fixed domain is shown in yellow. (b) shows only substrate-free. (c – f) show amino acids with measurable Rex, colored red, with the exception of residues between 180-209, near loop L8, which are shown in green. The classical N- and C-terminal domains are shown blue and sand. c & d are stereographic pairs with loop 8 residues labeled in panel d, and all others labeled in panel c. Panels d & f are rotated 90° with respect to panels c & e. e shows the interface between N- and C-terminal domains and location of N-terminal domain hinge. In all panels, substrates ADP, NO3 anion, and arginine are shown from the -bound structure to guide the eye.