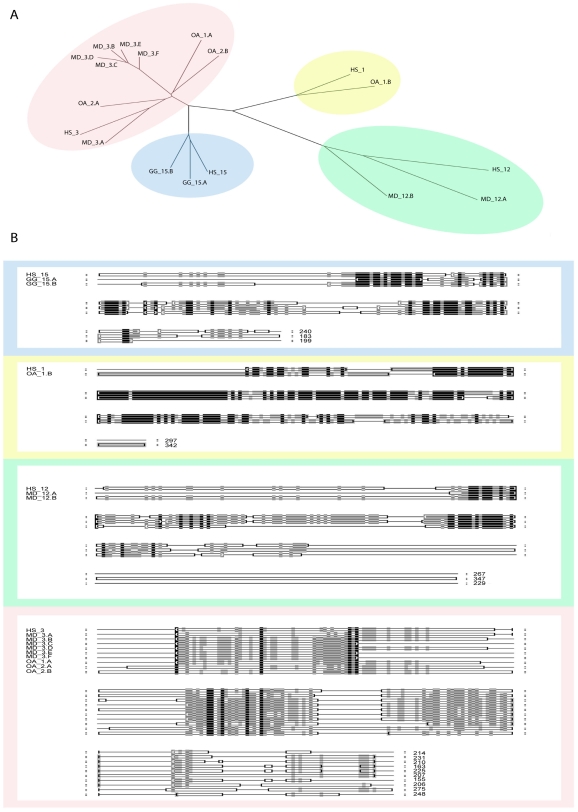
Figure 3. Tandem MS4A genes in G. gallus, M. domestica and O. anatinus.
The long MS4A protein sequences were cut into their subunit components and renamed with the suffix A through F to denote their respective position relative to the amino terminus. Alignment and phylogeny of these sequences was performed using ClustalX. The detailed alignments are shown in supplementary Figure S3. A. An unrooted phylogeny of the MS4A subunit sequences compared to full length human MS4A sequences. B. A schematic representation of the sequence alignments was generated using Genedoc. Shading indicates the degree of sequence conservation. Black shading indicates that the amino acid is conserved; grey indicates partial conservation and white indicates there is little to no sequence conservation at the indicated position.