Figure 7.
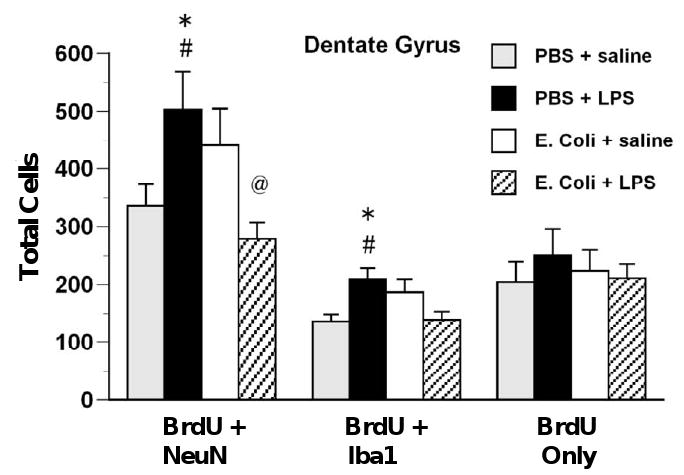
Immune challenge during adulthood decreases DG neurogenesis in rats treated neonatally with E. coli but increases neurogenesis and microgliogenesis in control rats. Rats received injections of either E. coli or PBS vehicle on P4 and BrdU on P4 and P5 and of either LPS or saline during adulthood. BrdU was injected immediately after LPS or saline and rats were killed 28 days later. In the DG, LPS injection during adulthood increased neurogenesis (BrdU + NeuN) in rats treated neonatally with PBS but decreased it in rats treated neonatally with E. coli. LPS during adulthood increased microgliogenesis (BrdU + Iba1) in rats treated neonatally with PBS. Values are means ± SEMs of 7 to 8 rats/group. * Significantly different from PBS + saline, p < .05. # Significantly different from E. coli + LPS, p < .05. @ Significantly different from E. coli + saline, p < .05
