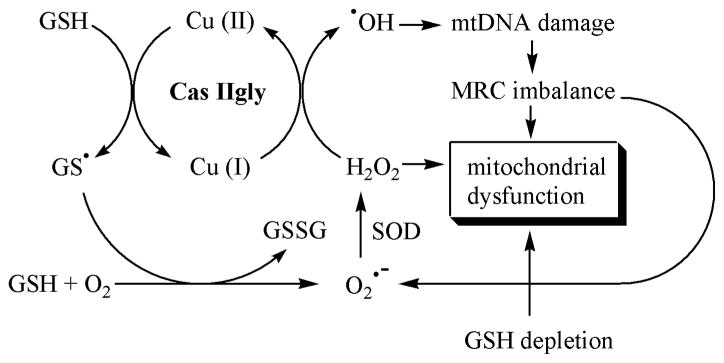
Figure 10.
Working hypothesis. Glutathione (GSH) reacts with Cas IIgly, resulting in reduction of the copper-complex and the formation of the glutathiyl radical (GS•), which can react with another GS• to give oxidized glutathione (GSSG), or with GSH and oxygen to give superoxide (O2•−) and GSSG. The formation of GSSG and O2•− can also result from redox-cycling of Cas IIgly with GSH and oxygen (not shown). Superoxide dismutase (SOD) converts O2•− into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which reacts with the reduced Cas IIgly to produce the hydroxyl radical (HO•). HO• can initiate mitochondrial DNA damage which translates in an imbalance of the expression of the proteins of the mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC) an d, in turn, into more ROS production. Mitochondrial dysfunction would result from both decreased levels of GSH and increased levels of H2O2.