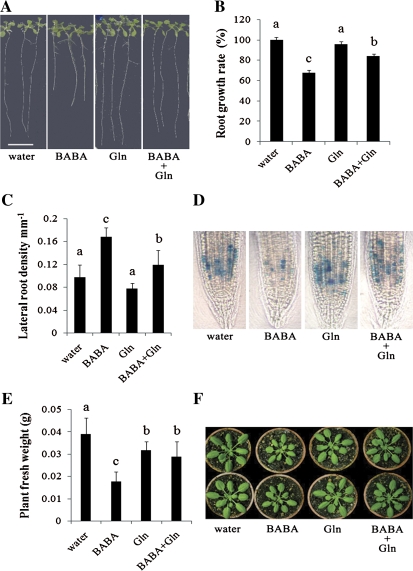
Fig. 3.
L-Glutamine partially rescues the BABA-mediated stress-induced morphogenic response. (A, B) Comparison of primary root length (A) and growth rate (B) of 15-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings grown on half-strength MS medium containing 75 μM BABA, 75 μM L-glutamine (Gln) or both L-glutamine and BABA (BABA+Gln). Scale bar=1 cm. (C) Lateral root density. Treatments were performed as in (A). The data are means ±SE (n >30). (D) L-Glutamine removes BABA inhibition on cell cycle activity. Cell cycle activity was evaluated by measuring primary root tip proCYCB1;1:GUS reporter activity (Negi et al., 2008). Five-day-old seedlings were grown in the presence of 500 μM BABA, 500 μM L-glutamine (Gln) or BABA and L-glutamine together (BABA+Gln) and stained for 2 h for GUS activity. (E, F) Fresh weight (E) and plant size (F) 3 d after treatment with 300 μM BABA, 10 mM L-glutamine (Gln) or both BABA and L-glutamine (BABA+Gln). Error bars are SD (n >30). Experiments were repeated three times. Representative results are shown. (B, C, D) Means with different letters are significantly different (P <0.05) based on a Least Significant Different (LSD) test.