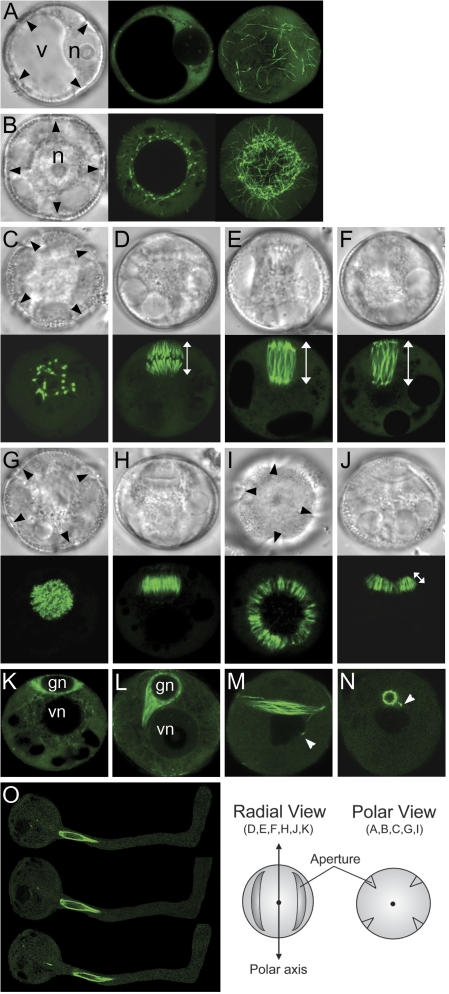
Fig. 2.
Live spores and pollen from ProNTM19-GFP::TUA6 transgenic line. Fresh spores and pollen viewed with DIC (grey) or with CLSM (green). (A, B) polarizing microspores, (C–J) microspores during mitosis, (K) early and (L) mid-bicellular pollen, (M, N) mature pollen. Microspores after equatorial nuclear migration (A) and after polar nuclear migration (B). Microspores are viewed as a single optical section (centre) or as projections of z-series (right) from the GP. (C–F) Microspores undergoing nuclear division are viewed from the GP (C) or from the radial wall (D–F). Mitotic spindles at metaphase (D), anaphase (E), and telophase (F). Images are single optical sections (C, E, F) or a projection of a z-series (D). (G–J) Microspores undergoing cytokinesis are viewed from the GP (G, I) or from radial wall (H, J). The phragmoplasts at early (G, H) or at later (I, J) stages. Images are single optical sections. (K–O) Fresh spores after microspore mitosis and mature pollen freshly dehisced or incubated in germination media are viewed. Early bicellular (K), mid-bicellular spores (L), mature pollen (M, N) or germinated pollen at three successive minute intervals, top to bottom (O). Images are single optical sections. Black arrowheads indicate apertures seen from the future GP. White arrowheads indicate a MT-rich tail connecting the germ cell and vegetative nucleus. v, Microspore vacuole; n, microspore nucleus; gn, germ cell nucleus; vn, vegetative nucleus. An orientation schematic for the images is shown. The white line with double arrow heads represents length measured for metaphase (D) and anaphase to telophase (E, F) spindles and for the phragmoplast (J).