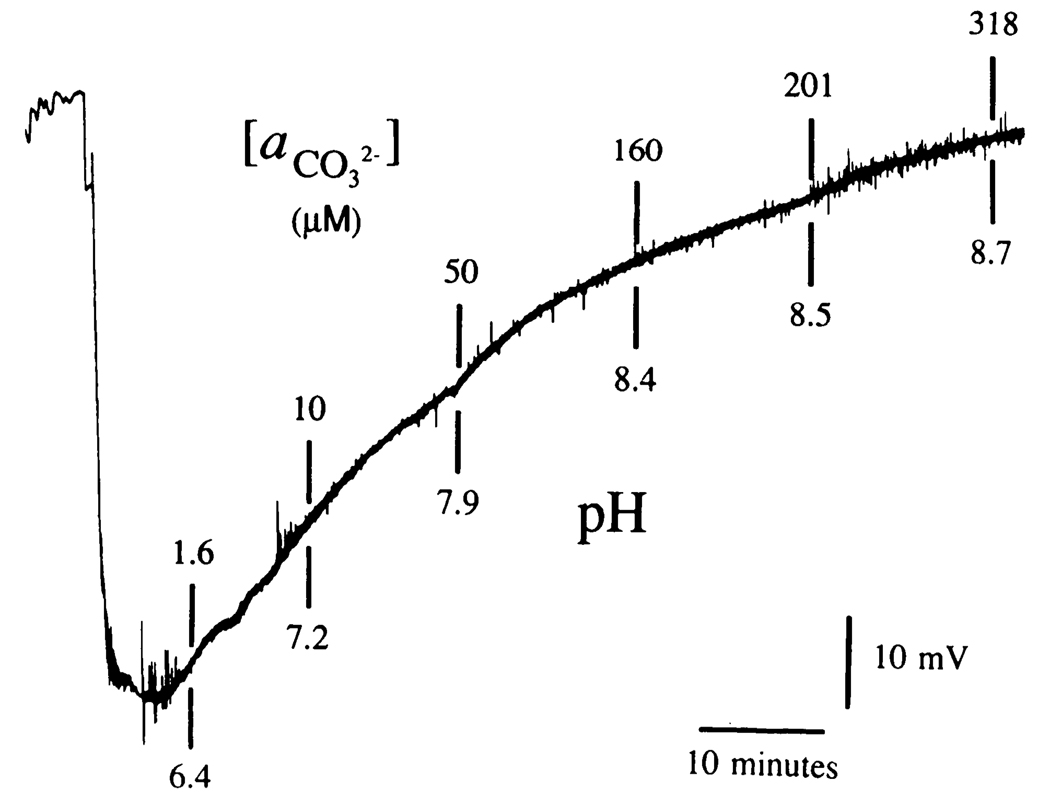
FIG. 2.
Potential response of a -sensitive ISM to changes in CO2 tension in NaHCO3. Record shown is the millivolt (mV) response of an ISM to changes in CO2 within a 10 mM (concentration) solution of NaHCO3. Such an alteration in gas tension will cause a small (i.e., µM) increase in but more than a 200% increase in . This simple, physicochemical fact can be used to determine if the ISM principally measures in a NaHCO3 solution. Here a 10 mM NaHCO3 solution was initially aerated with N2 (top left). Exposure to CO2 caused a prompt fall in solution pH to <6.4 (bottom left). At the same time ISM potential dropped by more than 50 mV, indicating that the ISM primarily measured and not . Finally, solution aeration was changed back to N2 (lower left of chart record). As solution CO2 tension dropped from this latter maneuver pH rose from <6.4 to >8.7 (as noted by specific solution pH measurements indicated below vertical lines). is shown above vertical lines.