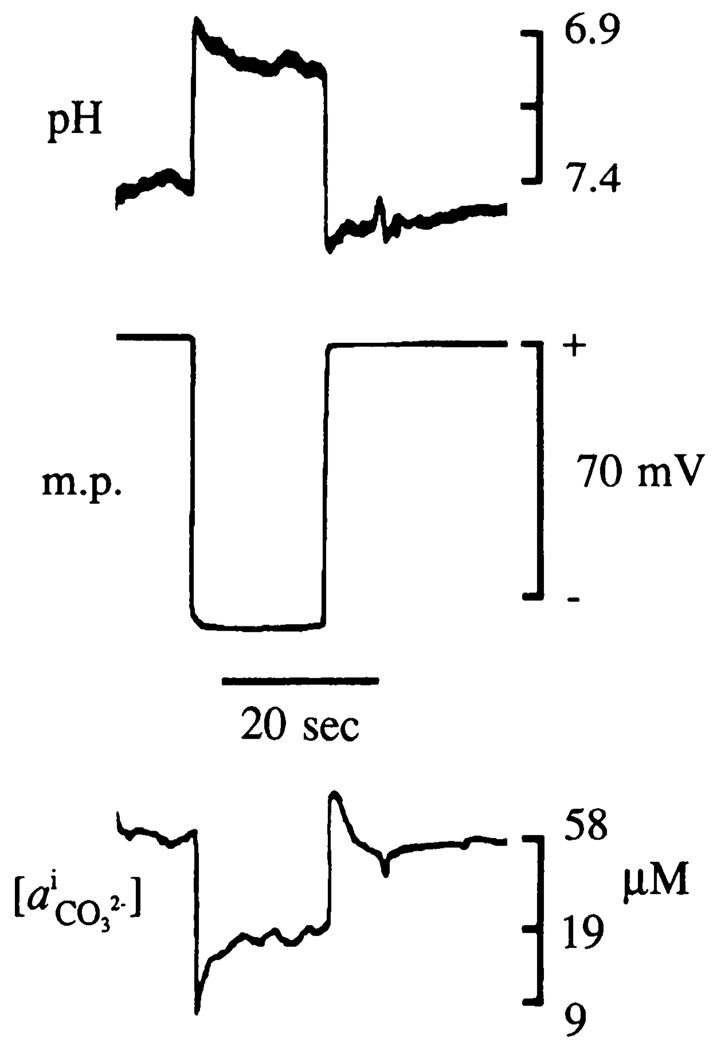
FIG. 3.
Intracellular record from skeletal muscle cell penetration with a triple-barrel ISM array consisting of pH-, -, and potential-sensing electrodes. Skeletal muscle cells in a temporalis muscle of an anesthetized and artificially ventilated rat were penetrated with a triple-barrel ISM array. Top: change in pH from interstitial level of 7.4 to that typically seen in skeletal muscle cells of 7.0 as array penetrates a cell. Middle: simultaneous measurement of membrane potential that in this instance exceeds 70 mV. Bottom: measured change in as array moves from interstitial to intracellular space. and pH measurements reached a new steady state <9 s after muscle cell penetration.