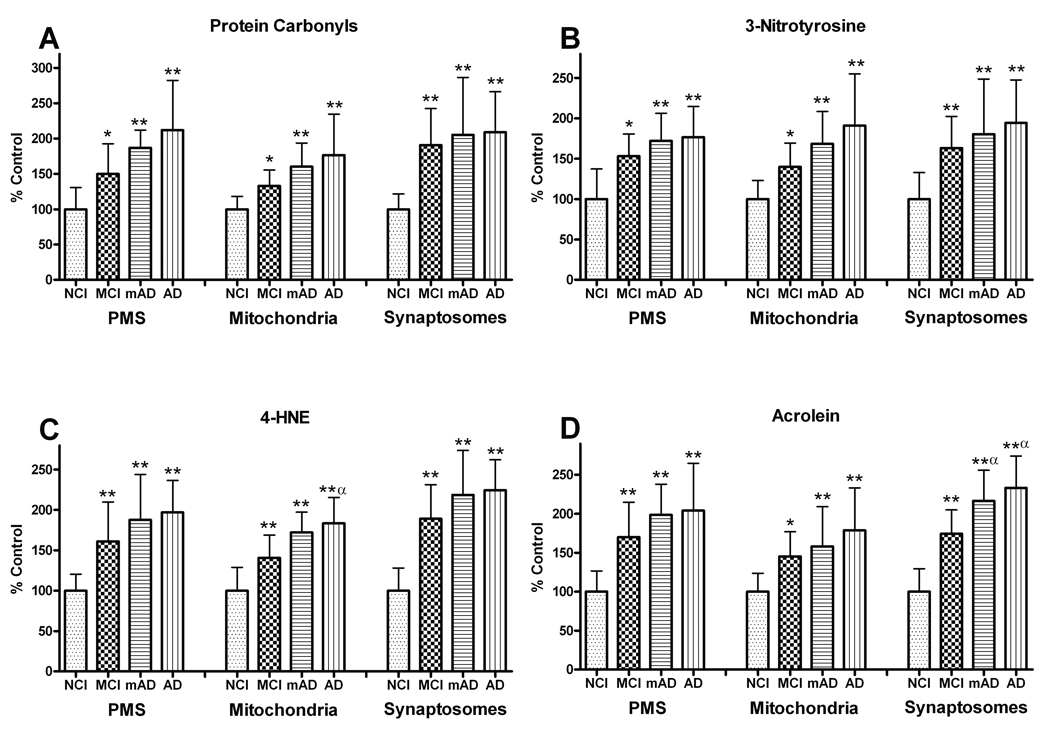
Figure 7.
Levels of protein modification were analyzed in post mitochondrial supernatant (PMS), mitochondrial, and synaptosomal fractions of the frontal cortex from non-cognitively impaired (NCI), mild cognitive impairment (MCI) mild Alzheimer disease (mAD), and AD subjects. (A) Protein carbonyl (PC) levels showed significant increases in all fractions of the frontal cortex with disease progression. (B) Significant changes in 3-nitrotyrosine levels mirrored the PC changes in all the fractions from MCI, mAD, and AD subjects. (C) 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and (D) acrolein levels showed significant increases in protein modification via lipid peroxidation. The significant increases in 4-HNE and acrolein were already present in MCI subjects, with the greatest elevations in the synaptosomal fractions. Each bar represents the group mean ± SD. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs. NCI; αp < 0.05 vs. MCI.