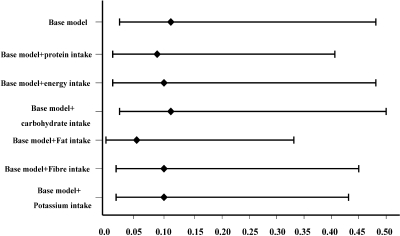
Figure 2.
Multivariate hazard ratio of average dietary sodium intake for CVD mortality and the impact of adjustment for dietary nutrients. Base model was adjusted for age, gender, body mass index, DM, the history of CVD, averaged variables including mean arterial pressure, Ca × P, hemoglobin, albumin, LDL, TKt/V, and Tccr. Other models were adjusted for covariates included in base model, sequentially added dietary nutrients including dietary protein, energy, carbohydrate, fat, fiber, and potassium intake. The P values for HRs of average dietary sodium intake for CVD mortality in these models were less than 0.05.