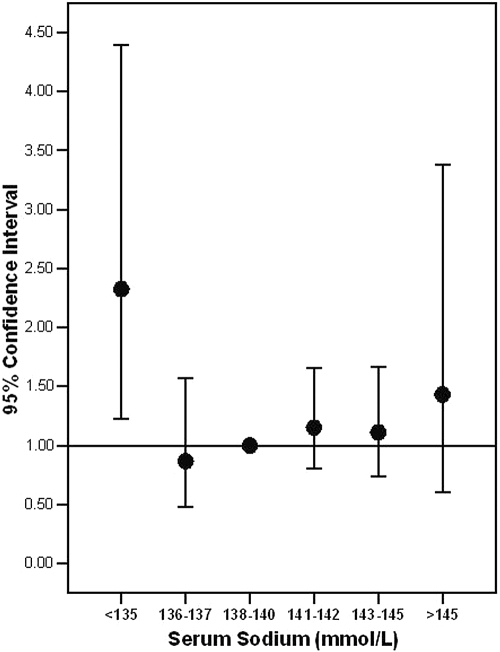
Figure 2.
OR (95% CI) of fracture occurrence by [Na+] category, adjusting simultaneously for age (years), T-score, CKD stage, osteoporotic risk factors (amenorrhea, low dietary calcium intake, high alcohol intake, maintenance steroids, ever having smoked, family history of osteoporosis, and history of liver disease), and osteoporosis therapy (use of calcium, vitamin D, antiresorptive therapy, hormonal replacement therapy).