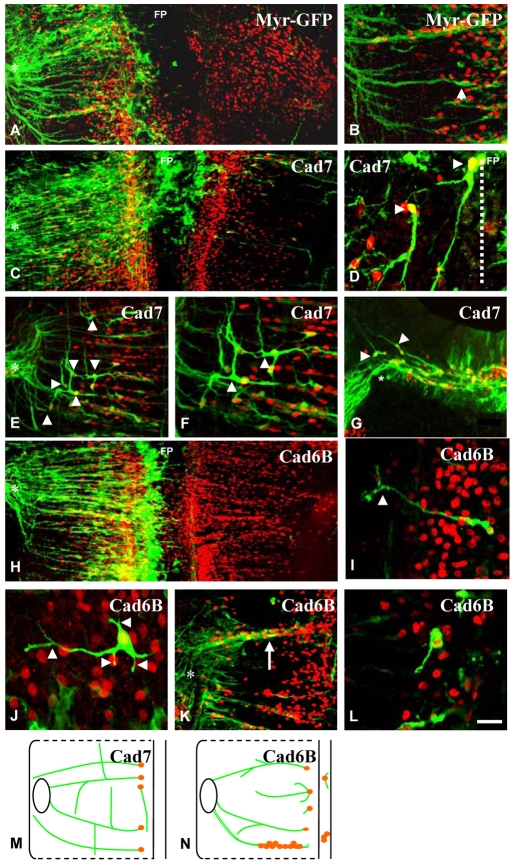
Fig. 5.
Effects of expression of full-length Cad7 and full-length Cad6b constructs in the chick hindbrain. (A-L) E4 hindbrains immunostained with anti-Islet1/2 (red) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies to detect electroporated neurons. Hindbrains were electroporated with myr-GFP control, Cad7 and Cad6B constructs as labelled. All panels show flat-mounts except G, which is a transverse section. Cranial motor axons project in a ventral-to-dorsal direction in controls (arrowhead in B). Medial is to the right and lateral to the left in all panels except A, C and H, which show both sides of the hindbrain. In Cad7-expressing hindbrains, axons project longitudinally (arrowheads in D-F). (F) A high-magnification image of E. In Cad6B-expressing hindbrains, cranial motor axons ectopically branch (I, arrowhead), extend multiple axons (J, arrowheads), aggregate at rhombomere boundaries (white arrow in K), and stall adjacent to the motor column (L). Asterisks indicate exit points. FP, floor plate. (M,N) Diagram of the behaviour of cranial motoneurons electroporated with full-length Cad7 (M) or full-length Cad6B (N). Scale bar: in L, 50 μm for A,C,E,H,K, 75 μm for B,F, 30 μm for G, and 15 μm for D,I,J,L.