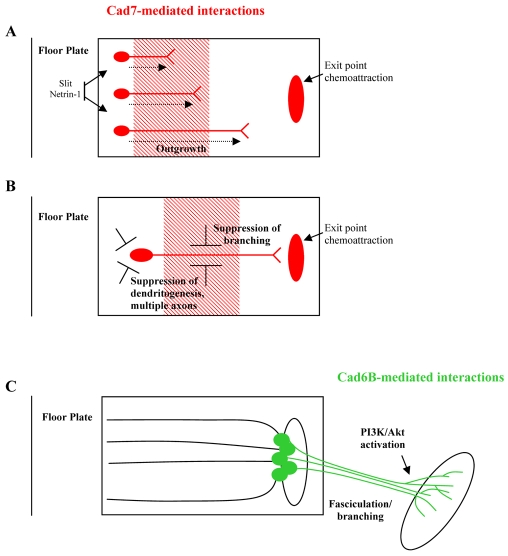
Fig. 8.
Model for the role of Cad7- and Cad6B-mediated interactions during BM neuron development in chick. (A-C) Flat-mount hindbrains showing the outgrowth of cranial BM neurons towards their exit points at ∼E3 (A) and ∼E4 (B) and their extension into the periphery at ∼E5 (C). (A) Cad7-mediated interactions (red) promote the early motor axon outgrowth. (B) Cad7-mediated interactions promote axon polarisation and suppress axon branching. (C) Cad6B-mediated interactions (green) promote branchiomotor/visceralmotor axon branching as they approach the branchial arch muscle plate, thus ensuring individual muscle masses are innervated. Cad6B branching is dependent upon the PI3K/Akt pathway.