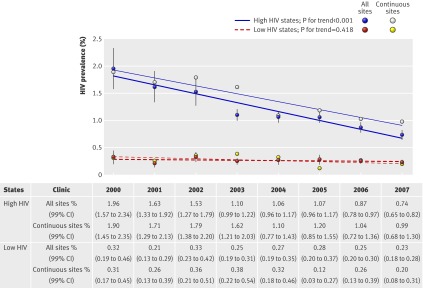
Fig 7 Trends in HIV prevalence among pregnant women aged 15-24 from 2000-7 in high and low HIV states. Low HIV states exclude northeast states (about 1.2% of India’s population), as injecting drug use dominates transmission in this region and may not be reflected well in trends of HIV in pregnant women. HIV prevalence estimates are age standardised to aggregate study population, 2000-7. All trend tests are adjusted for age, literacy, urban/rural residence, migrant status, state, clinic type, and year. Annual number of antenatal clinic attenders of all ages tested each year (2000-7) in high HIV states were 9599, 12 641, 15 030, 59 404, 63 105, 63 240, 64 283, and 67 265; numbers in low HIV states were 12 386, 22 386, 25 764, 44 790, 26 704, 26 248, 68 207, and 71 356. Numbers of surveillance sites in high HIV states were 36, 48, 54, 220, 234, 234, 235, and 242 (with 25 continuous sites); numbers in low HIV states were 56, 100, 114, 215, 118, 119, 339, and 345 (with 45 continuous sites)

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.