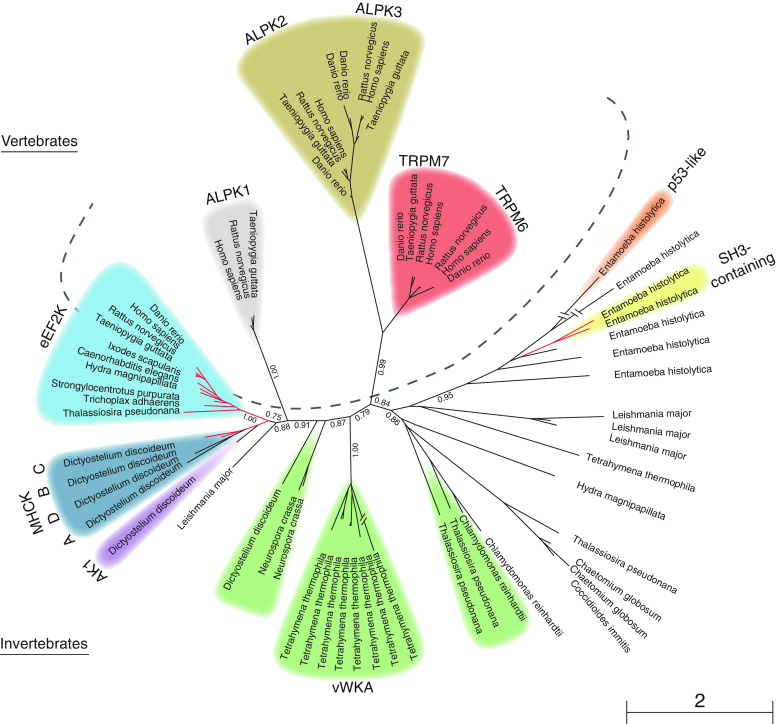
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the alpha-kinase family. A PSI-Blast [152] search was done, starting with the TRPM7 alpha-kinase domain and using three iterations, to detect all sequenced alpha-kinases. For those sequences that were detected with PSI-Blast, but that were not detected as having an alpha-kinase domain by SMART [151], reciprocal PSI-Blast searches were performed to ensure that they were indeed homologous alpha-kinases. From the results, species were included so that the major eukaryotic taxa with alpha-kinases would be represented in the tree. Selected sequences were then aligned using ClustalW2 [153]. A phylogenetic tree was generated using PHYML [154] as implemented in Seaview [155]. Bootstrap values of the major branches are indicated. The dashed line separates vertebrate from invertebrate alpha-kinases. Red branches indicate N-terminal alpha-kinases. Alpha-kinases with a typical subdomain architecture are indicated in the colors that refer to the schematic representations in Table 1