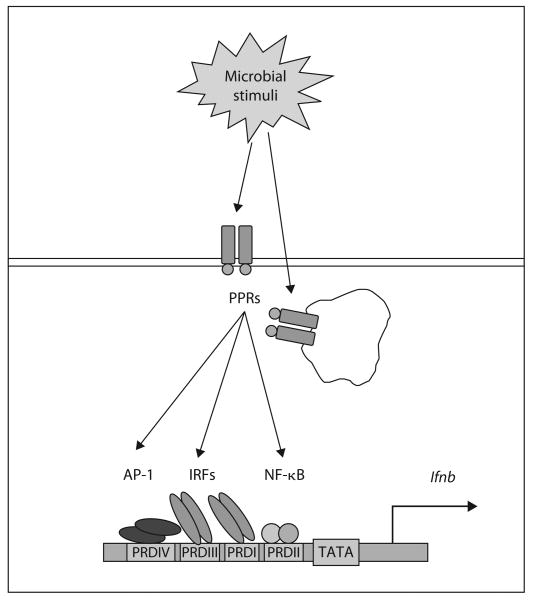
Fig. 1.
Type I IFN induction by microbial stimuli. The ifnb1 promoter region is shown schematically. Microbial stimuli interact with extra- or intracellular PPRs and lead to the activation of NF-κB, AP-1 and IRFs transcriptional factors which bind to specific PRDs on the promoter region of IFN-β gene and driving the gene expression. The promoter contains four PRDs. PRD I and III are the binding sites for IRFs, PRD II binds NF-κB and PRD IV binds AP-1.