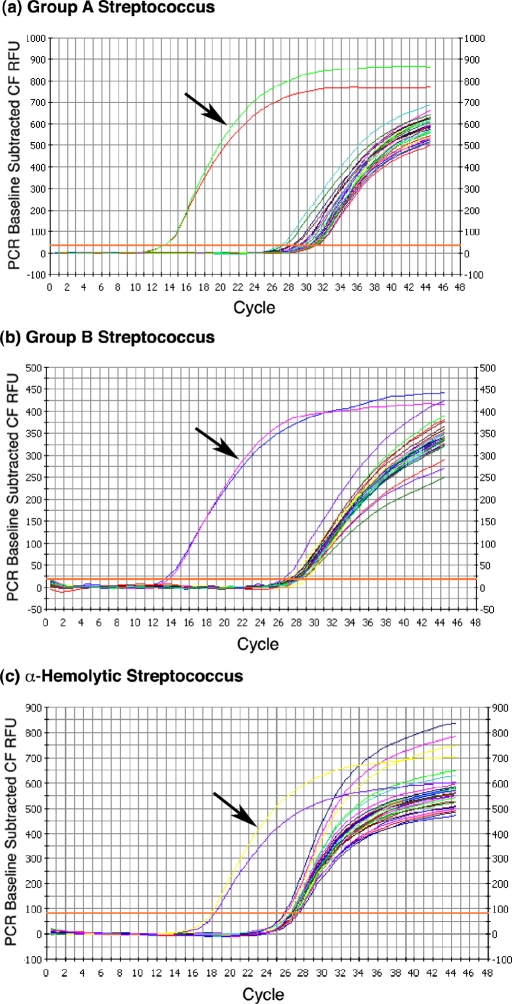
Fig. 2.
Species-specific rRNA-based RT-qPCR. rRNA RT-qPCR analysis of RNA samples was performed on total RNA obtained from fifteen clinically relevant bacterial pathogens with use of group-specific primers. All organisms were grown to a concentration of 1 × 107 CFU/mL prior to total RNA extraction. The three graphs show the polymerase chain reaction outcome with use of primers designed for (a) group-A Streptococcus, (b) group-B Streptococcus, and (c) α-hemolytic Streptococcus. Initiation of the logarithmic rise in the analysis curve at a lower cycle indicates identification of the labeled species. Arrows indicate resultant Ct curves from polymerase chain reactions with use of RNA from the intended target organisms. All reactions were run with duplicate samples.