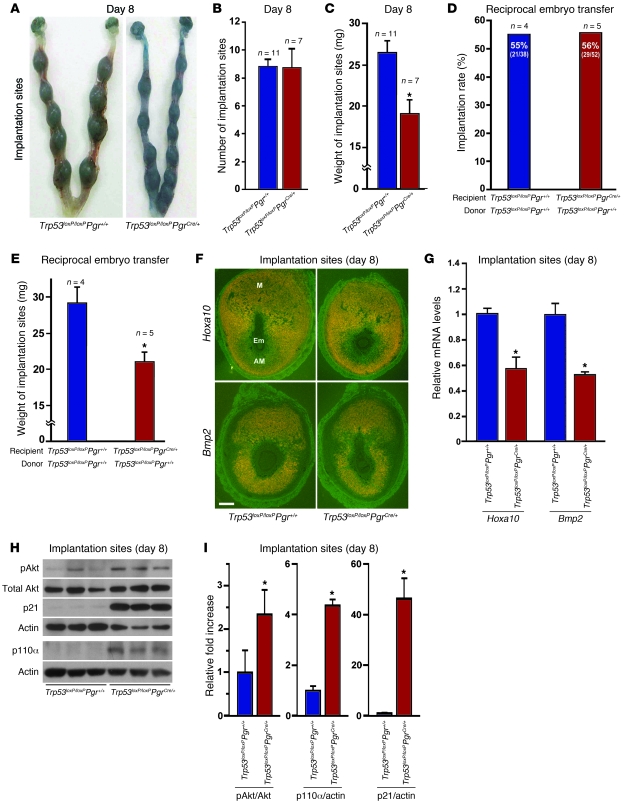
Figure 3. Uterine deletion of Trp53 restricts normal decidual growth.
(A) Representative photographs of day 8 pregnant implantation sites in Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+ and Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ mice. (B and C) Number and weight of implantation sites in Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+ and Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ mice on day 8 of pregnancy (mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05). (D and E) Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+ blastocysts were transferred into uteri of Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+ or Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ recipients on day 4 of pseudopregnancy. The number and weight of implantation sites were evaluated on day 8, 4 days after embryo transfer (mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05). Numbers in parentheses denote the ratio of implantation sites/total blastocysts transferred. (F) In situ hybridization of Hoxa10 and Bmp2 in Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+ and Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ uteri on day 8 of pregnancy. Em, embryo; M, mesometrial pole; AM, antimesometrial pole. Scale bar: 200 μm. (G) Northern hybridization of Hoxa10 and Bmp2 in day 8 uteri of Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+ and Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ dams. In each group, 2–3 independent samples were examined (mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05). (H and I) Loss of p53 upregulated pAkt, p110α, and p21 levels in day 8 implantation sites. As assessed by Western blotting (H), quantitatively analyzed band intensities of pAkt were normalized against total Akt, and those of p110α and p21 were normalized against actin (I). In each group, 3 independent samples from different mice were examined (mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05).