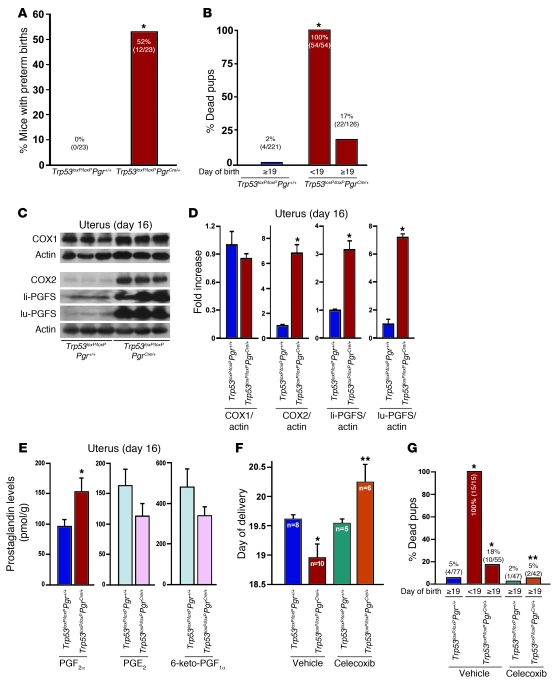
Figure 6. Uterine deletion of Trp53 promotes preterm birth through COX2/PGFS/PGF2α pathway.
(A) Preterm birth (deliveries earlier than day 19) occurred in 52% of Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ dams (*P < 0.05). Numbers in parentheses denote the ratio of dams with preterm birth/total dams. (B) All pups born before day 19 were dead around the time of delivery or died immediately after birth (*P < 0.05 versus Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+). Numbers in parentheses denote the ratio of dead pups/total pups. (C and D) Levels of COX2 and PGFS were upregulated in day 16 uteri lacking p53. (C) Uterine samples from which placentas and fetuses had been removed were used for Western blotting, and (D) quantitative analysis of band intensities were all normalized against actin (mean ± SEM of 3 independent samples from different mice; *P < 0.05). (E) Conditional loss of uterine p53 upregulated PGF2α levels in day 16 uteri. A total of 15 independent samples from 3 different mice were evaluated (mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05). (F and G) Preterm birth and neonatal deaths in Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+ mice were reversed by oral gavage of celecoxib (10 mg/kg/dose, administered twice) on day 16. In G, numbers in parentheses denote the ratio of dead pups/total pups. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle-treated Trp53loxP/loxPPgr+/+; **P < 0.05 versus vehicle-treated Trp53loxP/loxPPgrCre/+.