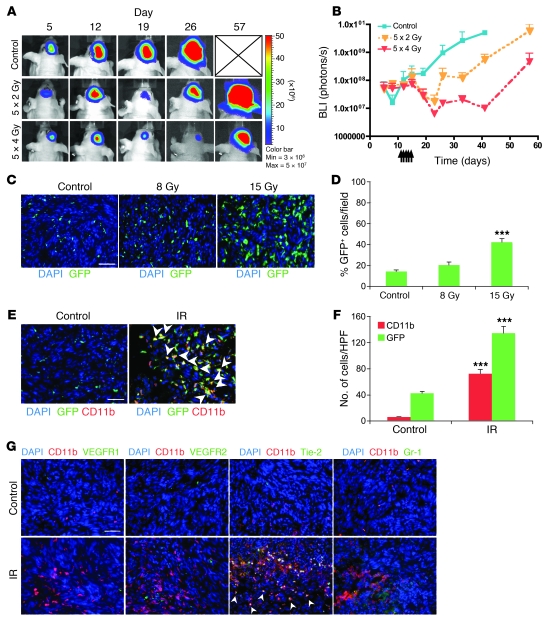
Figure 1. Irradiation promotes homing of BM-derived CD11b+ myeloid monocytic cells into GBM.
(A) Representative bioluminescent images of mouse heads with or without fractionated irradiation. Firefly luciferase–transduced U251 (U251/pFB-Luc) tumors were implanted i.c. and were irradiated from day 11 to day 15. 5 × 2 Gy, 2 Gy irradiation 5 times daily. (B) Tumor radioresponse was measured by BLI (n = 5 per group). Error bars indicate SD. (C) Radiation induced the influx of BMDCs into the U251 i.c. tumor. GFP-BM–transplanted nude mice received whole brain irradiation at 0, 8, or 15 Gy on day 22. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Quantification of GFP-BM influx into the tumor. Error bars indicate SEM. ***P < 0.001 versus control. (E) Representative images of IHC for GFP-BM cells and CD11b+ myeloid monocytic cells in U251 i.c. tumor before and after irradiation. Arrowheads indicate CD11b+ GFP-BM cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. (F) Quantification of CD11b and GFP-BM influx into the tumor. Error bars indicate SEM. ***P < 0.001. (G) Characterization of CD11b+ infiltrating cells into tumor after irradiation. Representative images of IHC staining for DAPI (blue), CD11b (red), and other markers (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, Tie-2, or Gr-1; green) in i.c. tumors after irradiation. Scale bar: 50 μm. IR, irradiation.