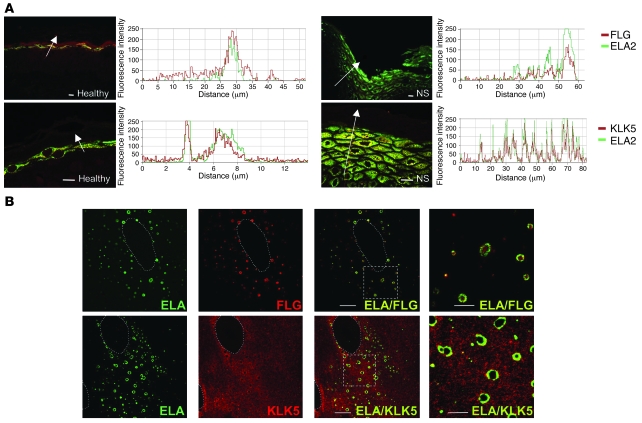
Figure 8. ELA2 colocalizes with filaggrin and KLK5 in differentiated keratinocytes and in vivo.
(A) Colocalization between ELA2 and SG-specific proteins in normal and NS skin sections. ELA2 staining (green) and FLG or KLK5 staining (red) were analyzed in confocal laser scanning microscopy. Graphs, representing the signal intensity from each protein along the arrow, show a perfect colocalization of both signals in normal as well as in NS epidermis in spite of the decreased filaggrin signal level. Scale bars: 25 μm. (B) Colocalization experiment of ELA2 with FLG or KLK5 in normal human keratinocytes differentiated in culture, analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. ELA2 staining is quasi-exclusively localized around the (pro-)filaggrin–containing keratohyalin granules. KLK5 staining spreads in the entire cytoplasmic compartment, with concentrated areas at the periphery of the nucleus and around keratohyalin granules, where KLK5 and ELA2 colocalized. Note the presence of some intense yellow dots at a distance from the keratohyalin granules. Dotted outlines define the nucleus of the cells. The 2 far-right panels (ELA/FLG and ELA/KLK5) represent higher magnifications of the regions delineated by the dotted squares. Scale bar: 10 μm.