Figure 1.
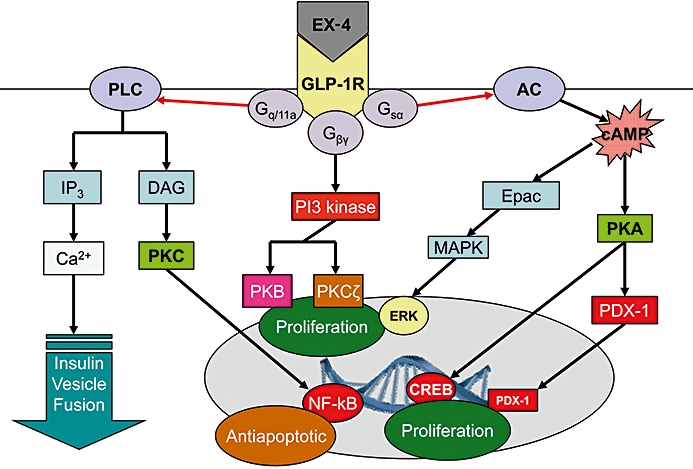
Intracellular events associated with stimulation of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors (GLP-1Rs). The receptor is G-protein coupled with a consequent rise in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Further intracellular events lead to nuclear changes and alterations in transcription. EX-4, exendin-4; GLP-1R, GLP-1 receptor; PLC, phospholipase C; IP3, inositol triphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa B; PI3 kinase, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; PKB, protein kinase B; PKCζ, protein kinase C-zeta; AC, adenylate cylase; Epac, exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; PDX-1, pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1; CREB, cyclic AMP response element binding protein.
