Figure 6.
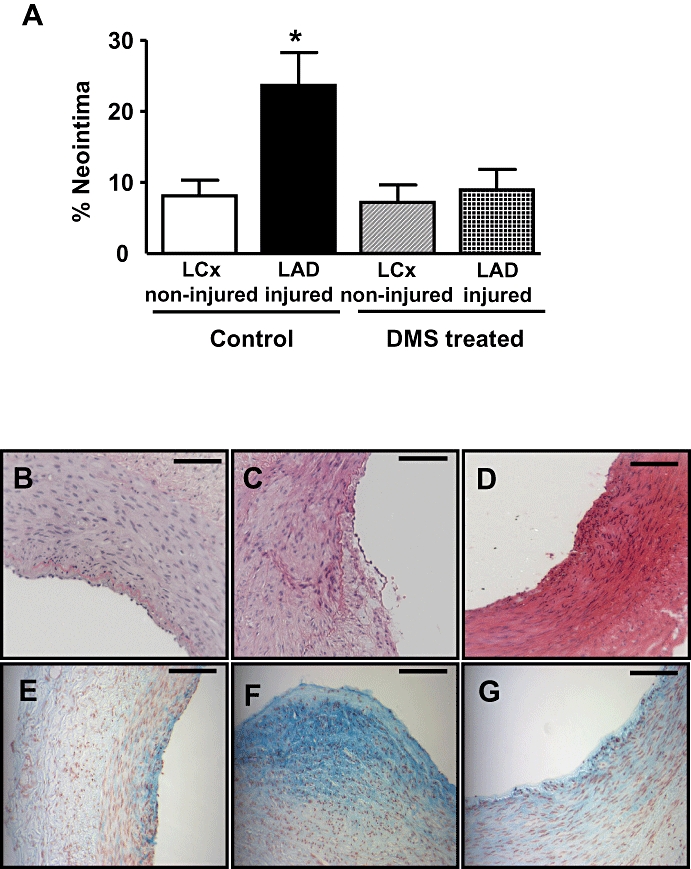
Effect of DMS on neointimal formation in vivo. (A) Neointimal formation was quantified in sections of coronary arteries isolated from non-injured LCx and balloon-injured LAD arteries 28 days after surgery. Neointima was calculated as a percentage of the total neointima and medial area. Local infusion of DMS (5 mL of 25 mM solution, where indicated) following balloon injury significantly reduced neointimal formation. (Values shown are mean + SEM; n = 6–7. *P ≤ 0.05 compared to the other three groups of arteries using one-way anova followed by Tukey's test.) (b–g) Photomicrographs of coronary arteries removed 28 days after angioplasty. Sections B–D were stained with haematoxylin and eosin, and sections E–G were stained with alcian blue. Scale bar represents 100 mm. Panels (B) and (E) represent a small spontaneous lesion in the non-injured LCx (vehicle-infused animals). Panels (C) and (D) represent sections isolated from balloon-injured LAD coronary artery (vehicle-infused animals). Panels (D) and (G) show that neointimal formation was markedly reduced in sections isolated from balloon-injured LAD coronary arteries in DMS-infused animals.
