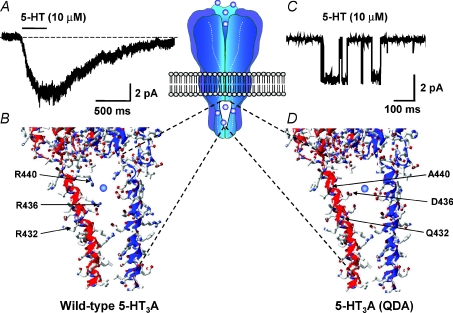
Figure 4. The influence of amino acid residues within the MA stretch upon the γ of the human 5-HT3A receptor.
A, inward current response evoked by 5-HT applied to an outside-out membrane patch excised from a HEK-293 cell expressing the human homomeric 5-HT3A receptor. The patch was voltage-clamped at a holding potential of −60 mV. Note the absence of discernable single channel current events. B, homology model, constructed as described by Hales et al. (2006) from the 4 Å resolution structure of the Torpedo nACh receptor, of an intracellular portal of the homomeric 5-HT3A receptor illustrating the arginine residues that collectively influence γ. Note that the side chains of R436 and R440 are predicted to face into the portal to impede cation ion flux. C, single channel currents evoked by 5-HT applied to an outside-out membrane patch excised from a tsA-201 cell expressing the human 5-HT3A (QDA) receptor construct. The patch was voltage-clamped at a holding potential of −80 mV. D, homology model of an intracellular portal subsequent to the mutations R432Q, R436D and R440A (i.e. 5-HT3A (QDA)). Note that reduced steric hindrance to ion flux is predicted, together with a local electrostatic potential more conducive to ion permeation. The central inset schematically illustrates the location of the portals within the receptor.