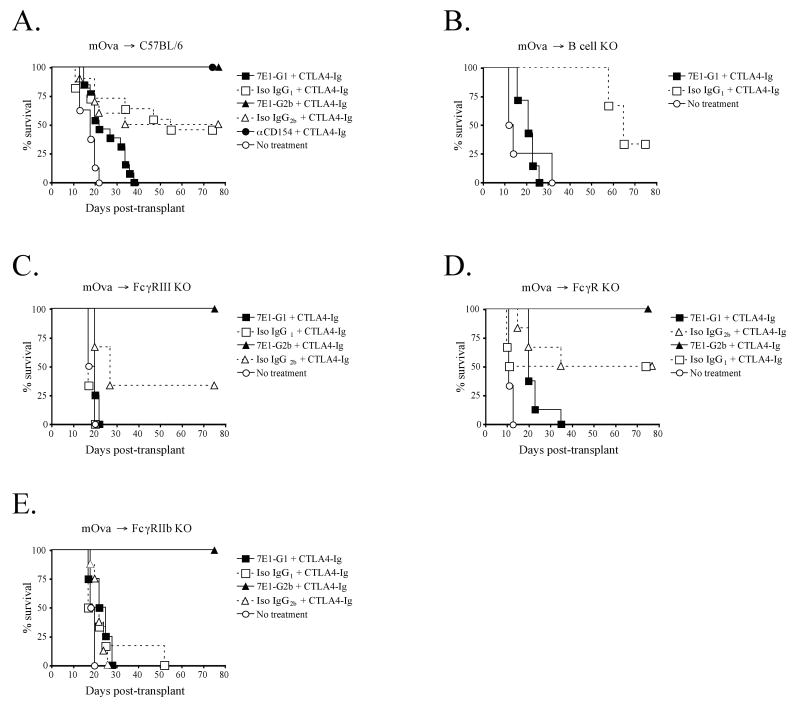
Figure 7. Fc-receptor and B cell involvement in mediating the differences seen between 7E1-G1 and 7E1-G2b.
(A) Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were transplanted with minor antigen mismatched mOVA (C57BL/6 background) skin grafts and treated with 500 μg of CTLA4-Ig and either 7E1-G1, isotype IgG1 control, 7E1-G2b, isotype IgG2b control, or anti-CD154 i.p on days 0, 2, 4, and 6. (B) B cell deficient mice were used as recipients of mOVA skin grafts with the same treatment regime as noted above, and showed graft survival similar to that of wild-type recipients. (C) FcγRIII deficient recipients did not show significant prolongation of mOVA skin graft survival when treated with CTLA4-Ig and 7E1-G1. (D) FcεRγI deficient recipients also did not show significant differences in the prolongation of mOVA skin graft survival as compared to wild-type recipients. (E) FcγRIIb deficient recipient mice, lacking the inhibitory Fc receptor, exhibited no diminution in the long-term graft survival observed in 7E1-G2b treated mice, while all other treatment groups promptly rejected their grafts.