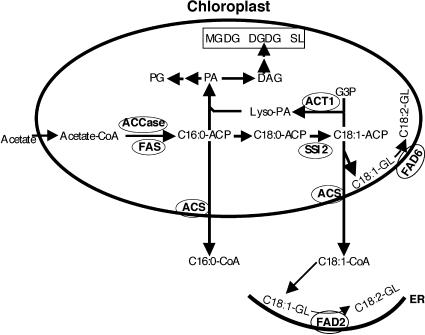
Figure 5.
Condensed Scheme for Lipid Biosynthesis in the Chloroplasts of Arabidopsis Leaves.
De novo FA biosynthesis from acetyl-CoA occurs exclusively in the plastids of all cells (represented by the oval). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) and fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex are key enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of C16:0 FA. Upon elongation to C18:0, this FA undergoes desaturation to C18:1. This step is catalyzed by the SSI2-encoded S-ACP-DES. The product of this reaction (C18:1-ACP) either enters the prokaryotic pathway of lipid biosynthesis through the acylation of glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) or is exported out of the plastids as a CoA thioester to enter the eukaryotic pathway. The acylation of G3P is catalyzed by an ACT1-encoded G3P acyltransferase. Desaturation of the C18:1 present on membrane glycerolipids (GL) is catalyzed by FAD2- or FAD6-encoded ω6 desaturases that are present on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) or the plastid envelop, respectively. Esterification of the CoA group is mediated by acyl-CoA synthetase (ACS). Symbols for various components are as follows: ACP, acyl carrier protein; C, carbon; DAG, diacylglycerol; DGDG, digalactosyldiacylglycerol; Lyso-PA, 1-acyl-G3P; MGDG, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol; PA, phosphatidic acid; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; SL, sulfolipid.