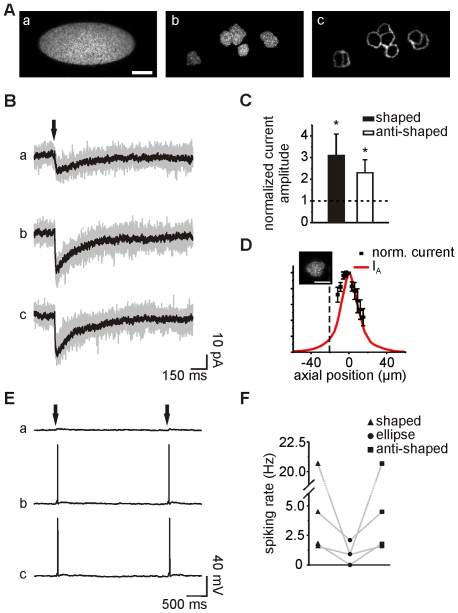
Figure 4. Electrophysiological recordings upon holographic photostimulation of multiple neurons.
A. Images of three pattern configurations obtained by exciting a thin layer of fluorescein: ellipse (a), shaped (b) and anti-shaped (c) patterns. Scale bar: 20 µm. B. Photolysis-evoked currents elicited in a recorded CA1 neuron held at −60 mV by uncaging MNI-glutamate in a group of target cells with the three patterns in (A), using an energy of 3.5 µJ at the sample plane. Individual sweeps (gray) and averaged currents (black) are shown (excitation densities: 0.9 nJ/µm2, 3.6 nJ/µm2 and 10 nJ/µm2 for the elliptic, shaped and anti-shaped patterns, respectively). C. Histogram of current amplitude increases obtained with shaped and anti-shaped patterns normalized by the currents obtained with an ellipse. D. Mean normalized amplitudes of photolysis-evoked currents obtained in five recorded neurons held at −60 mV and excited with a shaped pattern, while changing the focal plane of the objective with steps of 3 µm. The top of the slice is indicated by the black dashed line. The theoretical axial distribution of light (IA) for a shaped pattern is superimposed. Scale bar for the inset: 10 µm. E. Photolysis-evoked responses recorded in the same cell as in (B) in current-clamp mode. F. Comparison of spiking rates obtained with the three pattern configurations in four distinct cells.