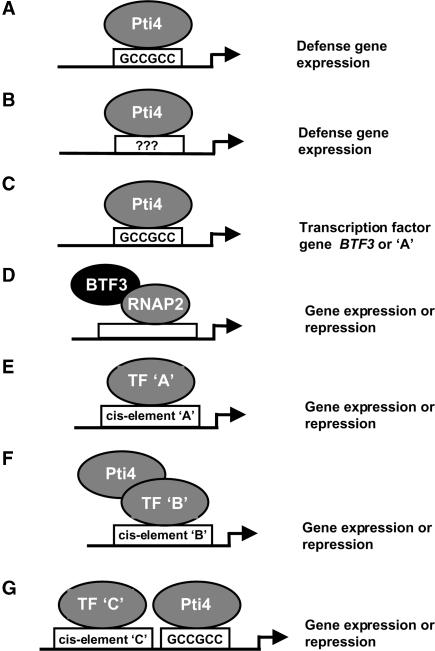
Figure 5.
Models for Pti4-Mediated Gene Expression.
Pti4 is postulated to regulate the expression of defense genes both directly via the GCC box (or a non-GCC box element) and indirectly via other transcription factors. Shown first are three “direct binding” models. In model A, Pti4 interacts directly with the GCC box to activate the expression of various defense-related genes. Model B shows that Pti4 might also bind directly to a currently unknown, non-GCC box element (shown as ???). In model C, Pti4 binds the GCC box present in the promoters of the BTF3 TF gene or another TF gene, designated TF A. In the next two “stepwise activation” models, the BTF3 protein associates with RNA polymerase II (RNAP2) to regulate gene expression (model D) or the TF A protein from model C binds the cognate cis element (A) present in the promoter of a defense-related gene (model E). In the “cooperative activation” model F, Pti4 interacts physically with another basally expressed transcription factor (TF B), and this interaction facilitates the expression of genes whose promoter contains a cis element bound directly by TF B. Finally, in the “tandem binding” model G, gene expression occurs upon binding of the GCC box by Pti4 and of another non-GCC box by a non-ERF TF. See Discussion for further details.