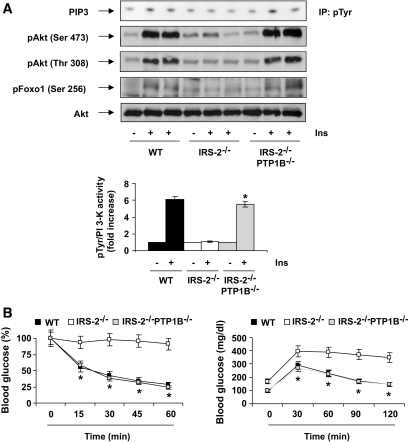
FIG. 1.
PTP1B deficiency recovers PI 3-kinase/Akt/Foxo1 insulin signaling in the liver of IRS2-deficient mice. A: Wild-type (WT), IRS2−/−, and IRS2−/−/PTP1B−/− mice (n = 9 animals per genotype) were fasted for 4 h, injected intraperitoneally with PBS or human regular insulin (0.75 units/kg), and killed 15 min later. Livers were removed and total protein extracts were prepared. Then, 600 μg total protein were immunoprecipitated with anti-pTyr antibody and used for an in vitro PI 3-kinase assay. The conversion of PI to PIP3 in the presence of [γ32-P] ATP was analyzed by thin-layer chromatography. Total protein (50 μg) was analyzed by Western blot with the antibodies against phospho-Akt (Ser 473), phospho-Akt (Thr 308), total Akt, and phospho-Foxo (Ser 256). A representative experiment is shown from four independent experiments performed. The autoradiograms showing PI 3-kinase activity were quantitated by scanning densitometry. Results are expressed as fold increase of PI 3-kinase activity and are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, IRS2−/−/PTP1B−/− vs. IRS2−/−. B: ITT (intraperitoneal injection of 0.75 units/kg human regular insulin) and GTT (intraperitoneal injection of 2 g d-glucose/kg) tests in wild-type, IRS2−/−, and IRS2−/−/PTP1B−/− mice [n = 6–8 per genotype]). Animals were fasted for 4 and 20 h prior to insulin and glucose tolerance tests, respectively. For ITTs, results are expressed as mean ± SEM of percentage of initial blood glucose value. For GTTs, results are expressed as means ± SEM of blood glucose value (mg/dl). *P < 0.05, IRS2−/−/PTP1B−/− vs. IRS2−/−.