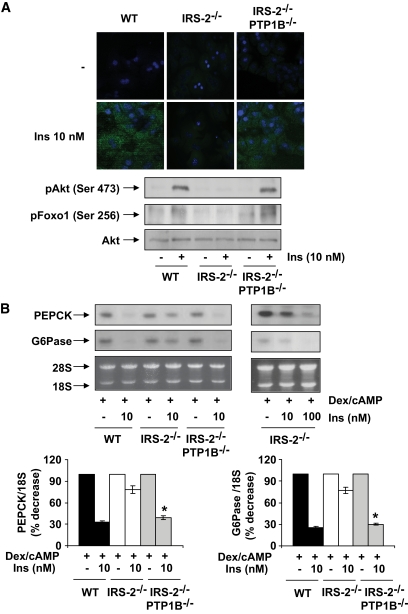
FIG. 2.
Recovery of insulin signaling and the inhibition of PEPCK and G6Pase in primary hepatocytes from IRS2−/−/PTP1B−/− mice. Primary hepatocytes obtained from mice of each genotype (wild type [WT], IRS2−/−, and IRS2−/PTP1B−) were cultured as described in research design and methods. A: Cells were serum starved for 4–6 h and further stimulated with 10 nmol/l insulin for 5 min. Upper panel: Cells were fixed in methanol (−20°C), and the generation of PIP3 was measured by confocal immunofluorescence with the anti–PIP3-FITC antibody. Representative images corresponding to primary hepatocytes isolated from one mouse are shown. Lower panel: Cell lysates were prepared, and total protein (50 μg) was used for Western blot analysis with the corresponding antibodies against phospho-Akt (Ser 473), phospho-Foxo (Ser 256), and total Akt. A representative experiment corresponding to primary hepatocytes isolated from one animal is shown from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. B: Cells were cultured in serum-free medium for 4–6 h and further stimulated with dex/cAMP (0.5 mmol/l dibutyril cAMP plus 1 μmol/l dexamethasone) in the absence or presence of insulin (10 or 100 nmol/l) for 6 h. At the end of the culture time, RNA was isolated and submitted to Northern blot analysis. A representative experiment corresponding to primary hepatocytes isolated from one mouse is shown. The autoradiograms corresponding to three independent experiments performed in hepatocytes were quantitated by scanning densitometry. The value of dex/cAMP-treated cells was set to 100%. Results are expressed as percentage of decrease by insulin of PEPCK and G6Pase mRNAs and are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, IRS2−/−/PTP1B−/− vs. IRS2−/−. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)