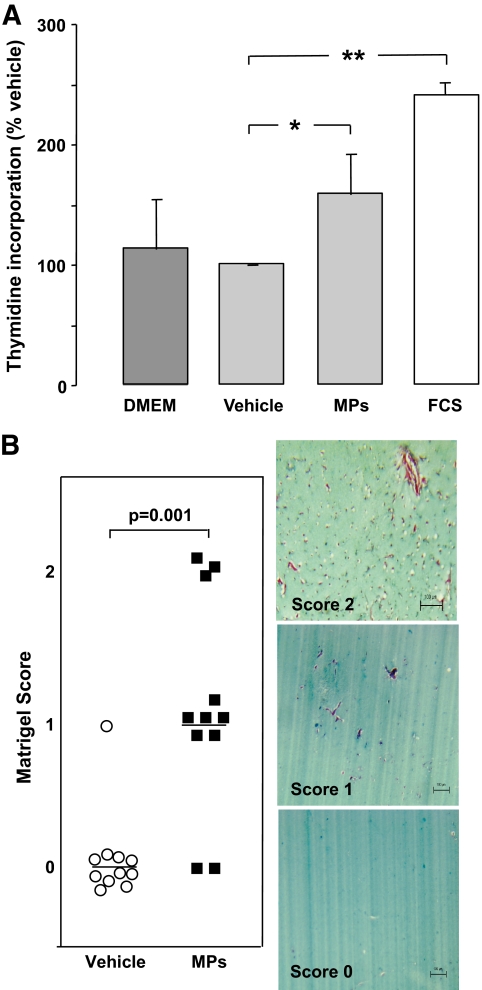
FIG. 5.
A: HUVECs proliferation assay (n = 4). 3H-thymidine incorporation with the vehicle (vitreous supernatant) was used as the baseline (100%). Levels of 3H-thymidine incorporation are represented with endothelium cell basal medium (Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium [DMEM]), FCS (2%), and vitreous microparticles (MPs). Vitreous microparticles (estimated as 65 CD144+ microparticles/μl for the endothelial subpopulation) increased 3H-thymidine incorporation by 1.6-fold compared with vehicle (vitreous supernatant without CD144+ microparticles) (*P = 0.029). FCS (10%) increased it by 2.4-fold (**P = 0.003). B: Matrigel scoring and angiogenesis assay. Serial sections of Matrigel were quantified by two independent pathologists. The presence of capillary structures with massive cells invasion was noticed (2). In some plugs, angiogenesis response was limited to cell invasion (1). Low concentration of vitreous microparticles (10 EMP/μl; 5,000 EMPs added to 500 μl Matrigel) induced endothelial cell migration (score 1; n = 6) and new vessel formation (score 2; n = 3) compared with vitreous supernatant (score 0; n = 12) (P = 0.001). (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)