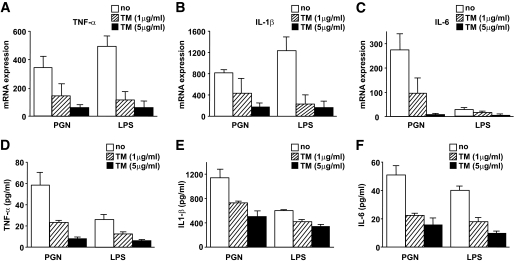
FIG. 6.
Expression of proinflammatory cytokines in response to TLR ligand stimuli decreased in human monocytes treated with tunicamycin (TM). Isolated human CD14+ monocytes were incubated in AIM-V culture media with tunicamycin (1 or 5 μg/ml) and stimulated using TLR ligands, PGN, and LPS for 6 h. A–C: RTD-PCR analysis showed that the expression of TNF-α (A), IL-1β (B), and IL-6 (C) was downregulated in human CD14+ monocytes treated with tunicamycin, especially at the higher concentration (5 μg/ml). D–F: ELISA showed that the production of TNF-α (D), IL-1β (E), and IL-6 (F) in culture media decreased in human monocytes treated with tunicamycin, especially at the higher concentration (5 μg/ml). Data are expressed as means ± SEM of four independent experiments. □, No treatment; ▨, treatment with tunicamycin (1 μg/ml); ■, treatment with tunicamycin (5 μg/ml).