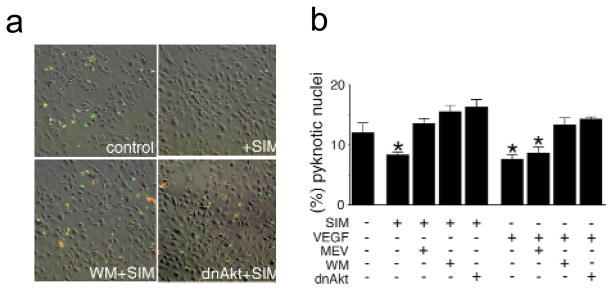
Fig. 4.
Simvastatin promotes endothelial cell survival through an Akt-dependent pathway. a, Representative images showing the cell-survival effects by simvastatin as detected by double-staining with annexin-V (green) and propidium iodide (red). HUVEC cultures were plated on chamber slides at a density of 4 × 104 cells/well. HUVEC were incubated in serum-depleted media for 3 h and subjected to stimulation with simvastatin (1 μM) for an additional 5 h. Parallel cultures were infected with Ad-dnAkt 24 h before the change to serum-free media. Some cultures were treated with 500 nM wortmannin (WM) for 1 h before each stimulation with simvastatin. b, Quantitative analysis of simvastatin-promoted endothelial survival by counting pyknotic nuclei stained by Hoechst 33342. HUVEC were examined in serum-free media as described in (a) to assess the effects of 1 μM simvastatin (SIM) or VEGF (100μg/ml) on survival. Data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4–6, *P < 0.05).