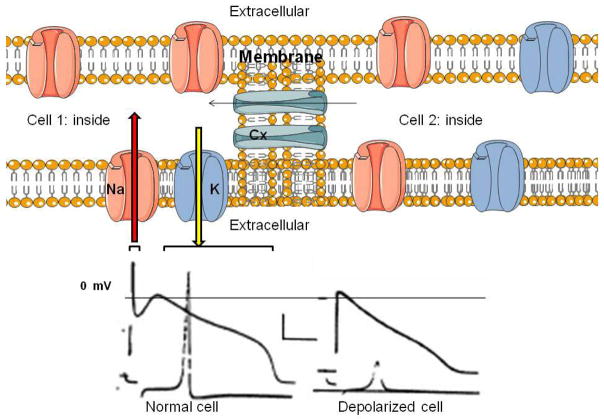
Figure 3.
Top: Two myocytes and their ion channels. Na and K channels are transmembrane structures carrying, respectively, inward (red arrow) Na current resulting in depolarization and outward (yellow arrow) K current resulting in repolarization. Connexins (Cx) populate the intercellular gap junctions and permit electron flow from one cell to another facilitating propagation of the cardiac impulse. Bottom: Schematic of action potentials from normal and depolarized (infarcted) ventricular myocytes. Upper traces are the action potentials and lower traces are the maximal upstroke velocity of phase 0 (V̇max) of the action potential reflecting rapid Na entry. Note the depolarized cell has a low V̇max and would be expected to result in slowed propagation. (Created using Servier technology; action potentials obtained from Lue and Boyden: Circulation: 1992: 85: 1175–1188, by permission).