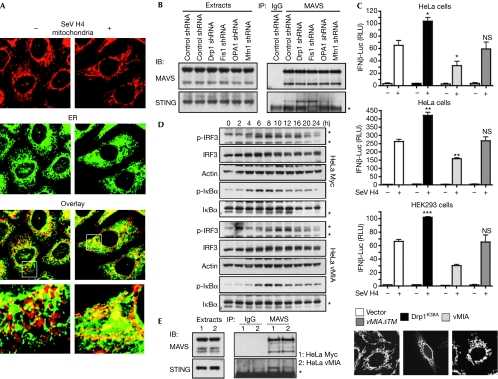
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial dynamics modulate the MAVS–STING association. (A) HeLa cells were infected or not with SeV H4. After 18 h, mitochondrial and ER morphology were examined by immunofluorescence. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with control, Drp1, Fis1, OPA1 or Mfn1 shRNA. After the selection of transfectants, MAVS was immunoprecipitated (IP) from cell extracts and the association with STING in each condition was examined by immunoblotting (IB). *IgG light chain. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) IFNβ-Luc or NF-κB-Luc reporter plasmids, as well as vMIA, vMIAΔTM, Drp1K38A or the vector alone, were transfected into the indicated cells. Sixteen hours later cells were infected with SeV H4 for 9 h or transfected with poly I:C for 8 h, and then IFNβ induction and NF-κB activation were assessed. ***P<0.001, **0.001<P<0.01, *0.01<P<0.05. NS, not significant (P>0.05). Mitochondrial morphology was also analysed by immunofluorescence. (D) Control HeLa cells (HeLa Myc) or HeLa cells stably expressing Myc-tagged vMIA (HeLa vMIA) were infected with SeV H4. At various time points after infection, p-IRF3, IRF3, p-IκBα and IκBα were analysed in cell extracts by immunoblotting. Actin was used as a protein loading control. *A probable non-specific protein band. (E) MAVS was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts of control HeLa cells or HeLa cells stably expressing vMIA and the association with STING was examined by immunoblotting. *IgG light chain. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. Drp1, dynamin-related protein 1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293; IFN, interferon; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IRF, IFN regulatory factor; Luc, luciferase; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signalling; Myc, myelocytose; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; OPA1, optic atrophy type 1; RLU, relative luciferase unit; SeV, Sendai virus; shRNA, short-hairpin RNA; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; vMIA, viral mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis.