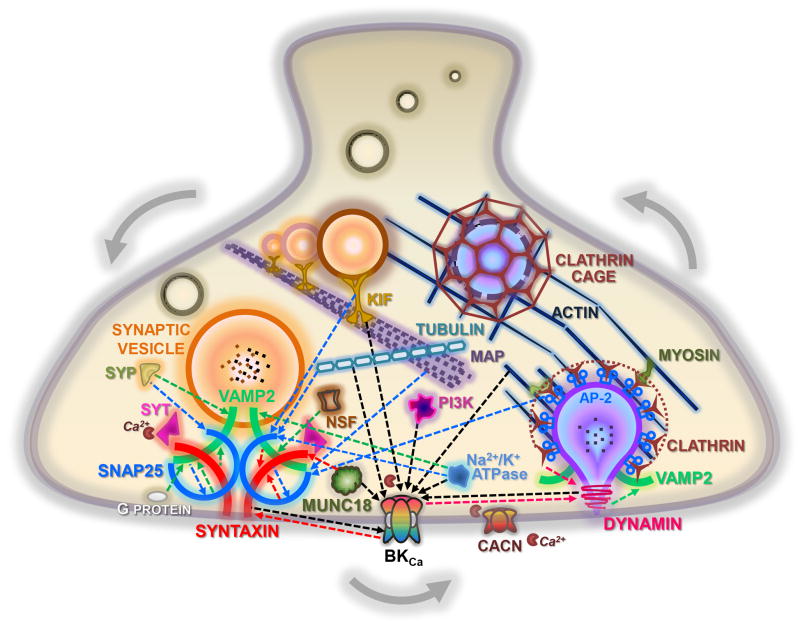
Figure 6. Provisional representation of a putative synaptic protein network.
A summary of the interactions shown in this study, derived from the BKCa channel alpha subunit, dynamin-1, SNAP-25, syntaxin-1A, and VAMP-2 immunoprecipitations from mouse cortex. Proteins are shown, as players in exocytic (left) and endocytic (right) pathways. Interactions are indicated by dashed arrows, whose colors and heads refer to the bait protein used to co-IP the partner. The calcium channels, synaptotagmin, and myosin proteins were not found in our studies, but are known to exist in a complex with one or more proteins that were identified in our screen. Additional experiments are required to verify the topology, molecular mechanisms, and functional significance of these interactions. CACN, voltage-gated calcium channels; KIF, kinesin family proteins; MAP, microtubule associated proteins; NSF, N-ethylmaleimide sensitive fusion attached proteins; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase protein family; SyP, synaptophysin; Syt, synaptotagmin.