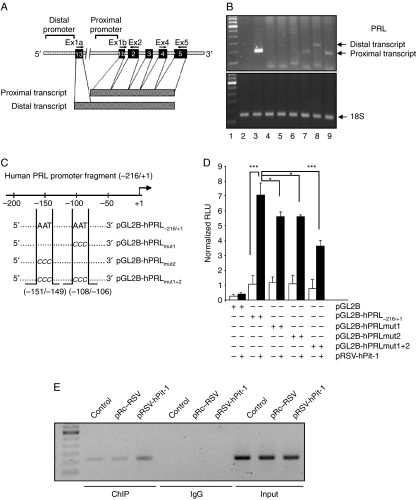
Figure 2.
PRL from MCF-7 cell line is identical to PRL of pituitary origin, and it is transcriptionally regulated by Pit-1. (A) Diagram of human PRL gene and promoter showing the location of the primers used in the RT-PCR assay as well as the proximal pituitary transcript and the distal extrapituitary transcript. (B) PCR products obtained from human pituitary gland, NIH-3T3, MCF-7, and HeLa cell lines using primers that amplified proximal pituitary transcript (194 bp) or distal extrapituitary transcript (275 bp). Lane 1, molecular weight marker; lanes 2 and 3, PCR product from human pituitary using PRL extrapituitary (negative control) or pituitary (positive control) primers respectively; lanes 4 and 5, PCR products from NIH-3T3 cells (used as negative control) using PRL extrapituitary or pituitary primers respectively; lanes 6 and 7, PCR products from MCF-7 cells using PRL extrapituitary or pituitary primers respectively; lanes 8 and 9, PCR products from HeLa cells using PRL extrapituitary or pituitary primers respectively (positive control). (C) Diagram of the proximal PRL gene promoter construct (pGL2B-hPRL−216/+1) and the mutated constructs (pGL2B-hPRLmut1, pGL2B-hPRLmut2, and pGL2B-hPRLmut1+2) showing the location of the Pit-1-binding sites and the mutated bases. (D) Either the wild proximal pituitary PRL promoter or a mutant PRL promoter fused to the pGL2 basic vector was cotransfected with the pRSV-hPit-1 expression vector into MCF-7 cells using FuGene reagent, and cells were then cultured for 48 h. Normalized relative luciferase units (RLU) were calculated as the ratio of luciferase activity in cells transfected with the wild or mutated constructs to the activity in the corresponding control cells. (*P<0.05; ***P<0.001 versus control cells). (E) Soluble chromatin prepared from control MCF-7 cells, cells transfected with the pRSV-hPit-1 vector, and cells transfected with the control vector (pRc/RSV) were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Pit-1 antibody or control IgG. The immunoprecipitated DNA was amplified by PCR using specific primers corresponding to the proximal PRL promoter (from −216 to +1, with respect to the start transcription site).