FIGURE 7.
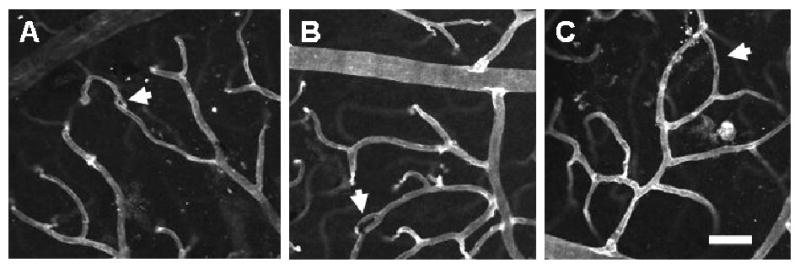
Exposure to whole-body hypoxia for 3 weeks results in vascular loop formation in the superficial networks of the adult mouse retina. High magnification (20×) confocal images obtained from retinal whole-mounts labeled with lectin (white) were used to examine the presence of vascular loops (arrows). Representative vascular loops illustrate the wide range of loop sizes observed in hypoxia-exposed retinas, which appear to correspond to the progressive stages of intussusceptive microvascular growth (Burri and Djonov, 2002), from the initial formation of a tissue pillar (A) to its subsequent elongation (B) and expansion to form larger vascular loops (C). The smallest loops detected (A) corresponded to the size and morphology of early tissue pillars previously identified in the developing amphibian retina (Dunlop et al., 1997). Scale bar = 50 μm.
