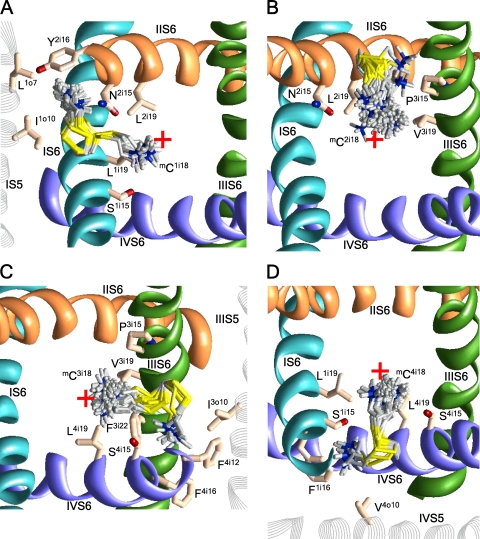
Figure 3.
The extracellular views of various orientations of mCi18 residues in Cav2.1. For clarity, the P loops are not shown. The red cross indicates the pore axis. (A) Cation–π interactions with Y2i16 stabilize the repeat interface orientation mC1i18; the pore orientations have higher energy. (B) In the most preferable conformations, mC2i18 is oriented in the pore. (C) Cation–π interactions with F4i12 and F3i22 stabilize orientation of mC3i18 in the repeat interface; the pore orientations are less preferable. (D) Both pore and repeat interface orientations of mC4i18 are energetically favorable.