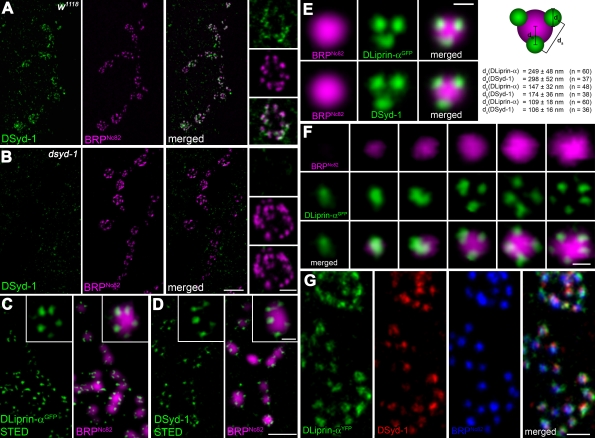
Figure 3.
DSyd-1 localizes to a subcompartment surrounding the AZ core. (A) Boutons of larval NMJ innervating muscle 6/7. Most DSyd-1 clusters are found associated with BRPNc82 signal, labeling AZs, as seen in high-magnification images (right). (B) There was no DSyd-1 staining at dsyd-1–deficient NMJs. (C) Single confocal slices of junctions expressing DLiprin-αGFP, as described in Fouquet et al. (2009). STED images of α-GFP labelings show DLiprin-αGFP as discrete spots arranged around the AZ core labeled by BRPNc82. (D) Single confocal slices of NMJs stained for endogenous DSyd-1 (STED) and BRPNc82 (confocal). Distinct separable DSyd-1 spots closely resembling DLiprin-α distribution are arranged around the AZ center. (E) Merged images of several aligned planar imaged AZs of moderate size associated with three DLiprin-α or DSyd-1 clusters. The image shows BRPNc82 in confocal resolution, α-GFP–labeled NMJs (for DLiprin-αGFP), or DSyd-1–labeled NMJs imaged with STED. The arrangement of DSyd-1 clusters resembles that of the DLiprin-α clusters. da, distance between single clusters associated with the AZ; db, distance between AZ associated cluster and AZ center; dc, diameter of clusters associated with AZs. (F) Single confocal slices of junctions expressing DLiprin-αGFP. STED images of α-GFP show DLiprin-αGFP as discrete dots arranged around the AZ core labeled by BRPNc82, ranging from one or two dots at small AZs to four or five dots at mature-sized AZs. (G) Triple labeling for DLiprin-αYFP, DSyd-1, and BRP. Bars: (A and B) 2 µm; (A and B, insets) 500 nm; (C and D), 1 µm; (C and D, insets): 250 nm; (E) 250 nm; (F) 250 nm; (G) 500 nm.