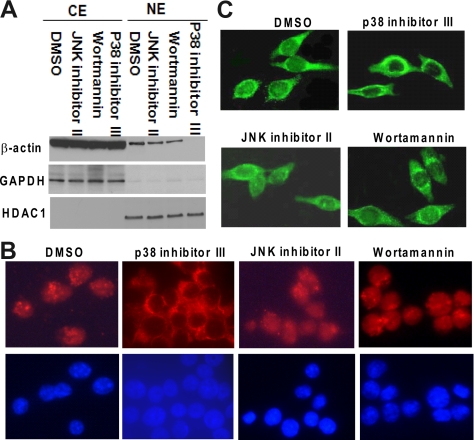
Figure 2.
Effects of JNK, PI3-K, or p38 MAPK inhibitors on PMA-induced translocation of β-actin into nucleus. (A) JNK inhibitor (JNK inhibitor II; 5 μM), PI3-K inhibitor (wortmannin; 1 μM), p38 MAPK inhibitor (p38 inhibitor III; 20 μM), or DMSO (the vehicle for inhibitors) was separately added to HL-60 cells 1 h before treating with PMA (10 ng/ml) for 48 h. (A) β-Actin levels in cytoplasmic fractions and nuclear fractions were monitored using Western blot analysis. The expression of the cytoplasmic marker GAPDH and nuclear marker HDAC1 was also monitored. (B) Effects of signal inhibitors on PMA-induced nuclear translocation of β-actin were detected by indirect immunofluorescence as described in Figure 1C. Red color represents β-actin; blue color depicts nucleus. (C) HL-60 cells expressing GFP-β-actin fusion protein were pretreated with kinase inhibitors or DMSO as described in A for 1 h and then cultured with PMA for 48 h. Fluorescence microscopy was used to observe the effects of kinase inhibitors on PMA-induced GFP-β-actin translocation.