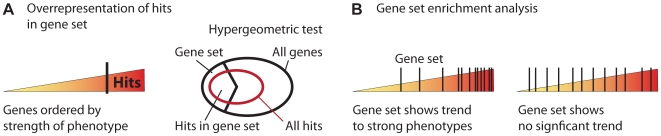
Figure 2. Functional annotation of hits by enrichment analysis.
(A) In the first approach [38] a cutoff is applied to select the hits with strongest phenotypes. A hyper-geometric test then evaluates if the overlap between the hits and a given gene set is surprisingly large (or small) compared to the overlap with a random set. (B) A second approach [35] does not need a cutoff. It maps the gene set (black bars) onto the observed phenotypes and quantifies if there is a significant trend or if the genes are spread out uniformly over the whole range.