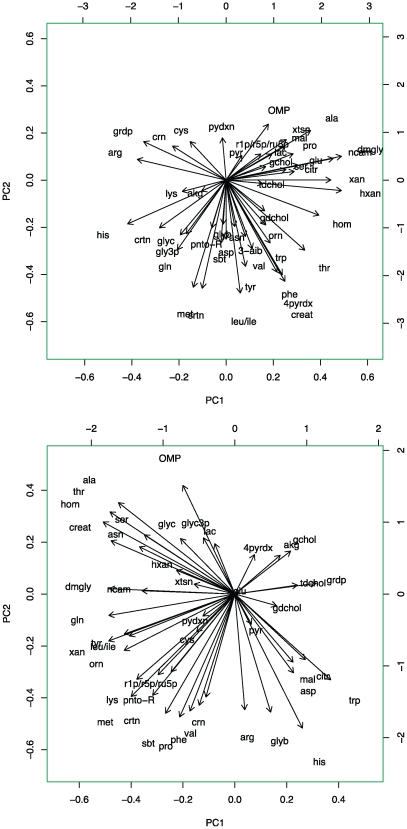
Figure 6. Principal component analysis of significantly changed metabolites (FDR<0.05) in NGT and IGT.
Panels (a) and (b) correspond to NGT and IGT, respectively. Principal component #1 largely corresponds to pathways regulated by hepatic SLC25A13 activity, including glycolysis (lac, pyr) and gluconeogenesis (ala, ser), nucleotide biosynthesis (OMP, r1p, hxan, xan, xtsn, ncam), bile salt (gchol, tdchol) and citrulline (citr) accumulation, and NAD+/NADH balance by malate shuttling (glu, akg, mal). Principal component #2 largely corresponds to System A and L amino acid transport.