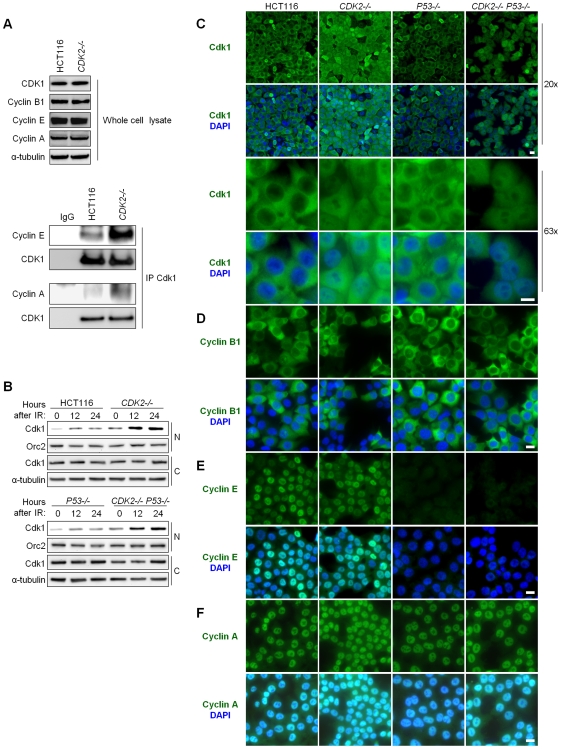
Figure 3. Aberrant localization of Cdk1 in Cdk2-deficient cells after IR treatment.
(A) Association between Cdk1 and cyclins E and A was determined by immunoprecipitation/immunoblot. Non-denatured cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Cdk1 or control (IgG) antibodies. Samples not subjected to immunoprecipitation were analyzed as whole cell lysate. Levels of Cdk1 and cyclins B1, E, and A were determined by immunoblot. (B) Cdk1 levels in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were determined by immunoblot at the indicated times after treatment with 12 Gy IR. Loading of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins was assessed by probing levels of Orc2 and α-tubulin, respectively. (C) Localization of Cdk1 by indirect immunofluorescence. Isogenic HCT116 cells were fixed 24 h after treatment with 12 Gy IR, stained with Cdk1 antibody (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Representative fields are shown under low (20×) and high (63×) magnification (scale bar, 50 µm under 20× magnification and 10 µm under 63× magnification). (D–F) Localization of cyclins by indirect immunofluorescence. Isogenic HCT116 cells were fixed 24 h after treatment with 12 Gy IR, stained with (D) cyclin B1, (E) cyclin E or (F) cyclin A antibodies (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Representative fields are shown under 40× magnification (scale bar, 10 µm).