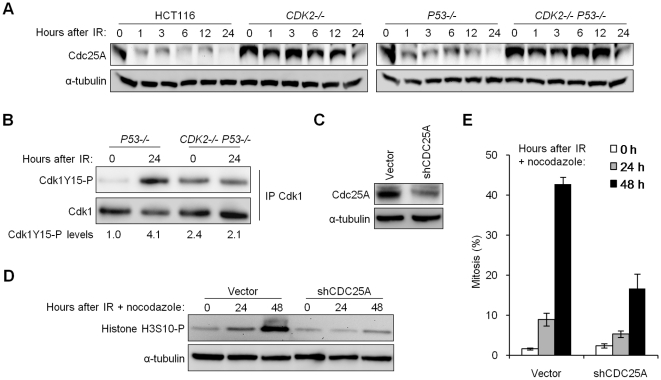
Figure 4. Impaired degradation of Cdc25A in Cdk2-deficient cells contributes to G2/M checkpoint defect.
(A) Isogenic HCT116 cells were harvested at the indicated times after treatment with 12 Gy IR. Cdc25A levels were determined by immunoblot. (B) Non-denatured cell lysates were collected before and 24 h after 12 Gy IR. Cdk1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and analyzed for phosphorylation on Y15 by immunoblot. Cdk1Y15-P was quantitated and normalized to total Cdk1. (C) Stable knockdown of Cdc25A in CDK2−/− P53−/− cells by retrovirus-mediated delivery of empty vector control (vector) or CDC25A shRNA (shCDC25A), assessed by immunoblot. (D) Cdc25A knockdown or control CDK2−/− P53−/− cells were treated with 12 Gy IR and 0.2 µg/ml nocodazole. Histone H3S10-P levels were determined by immunoblot. (E) Mitotic indices of Cdc25A-knockdown and control CDK2−/− P53−/− cells at the indicated times after treatment with 12 Gy IR and 0.2 µg/ml nocodazole. Error bars represent s.e.m. from six knockdown clones.